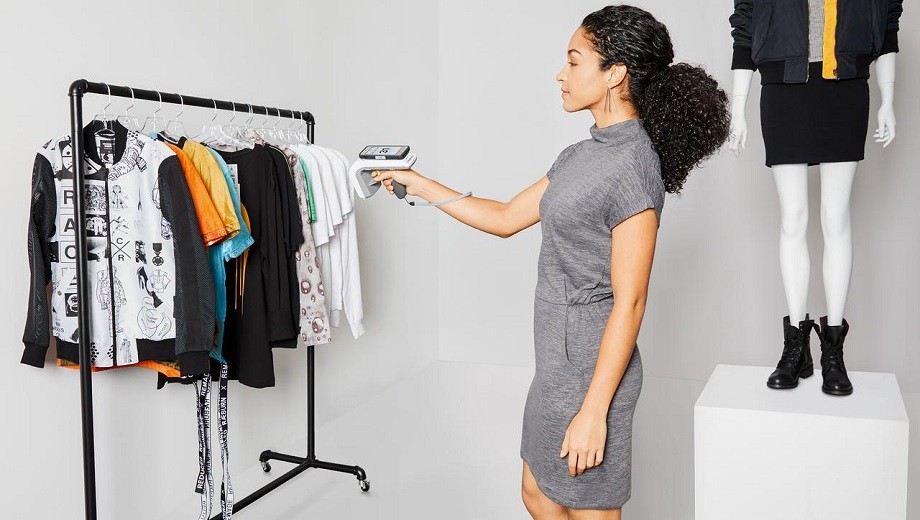
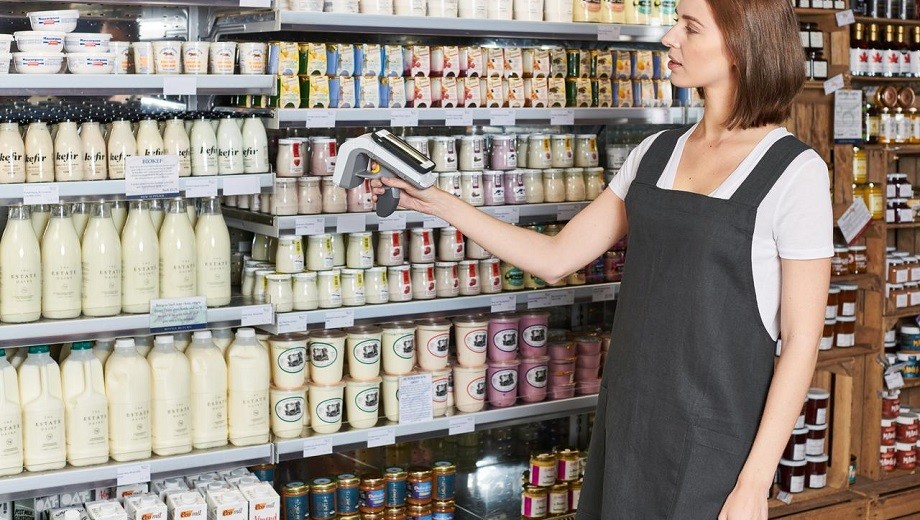
Choosing the appropriate RFID inlay and tag for your requirements can be a difficult task. Our product finder can be a useful starting point and our sales and customer team will be pleased to offer their assistance. In general, the target application and use case ultimately determine the RFID inlay and tag requirements, therefore when selecting the right RFID inlay or tag it is important to consider the following questions:
Q1: What is the product made of? (e.g. glass, plastic, metal)
Q2: Where will the tag be placed? (e.g. on the syringe, flagged, on the cap)
Q3: Will the product go through any process? (e.g. Sterilization, extreme temperatures)
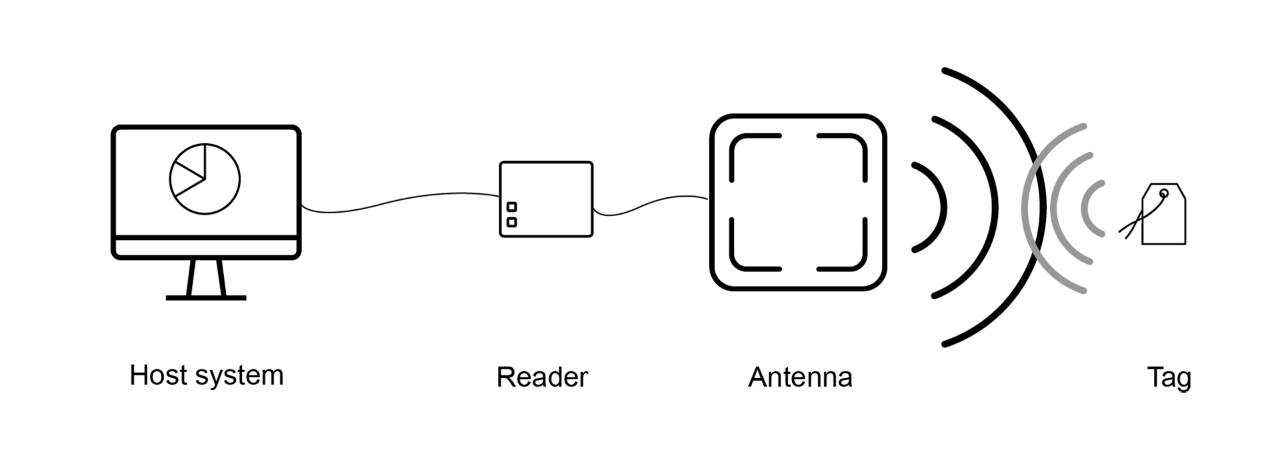
Q4: How will the RFID inlay be read? (e.g. handheld or fixed reader)
It's important to keep in mind that there are other factors that can influence the selection process as well, including:
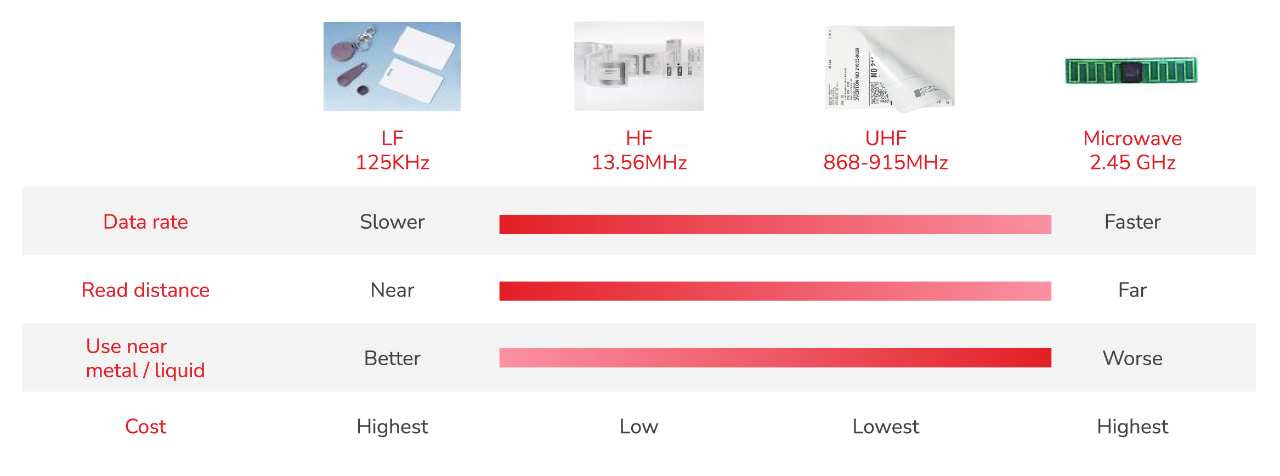
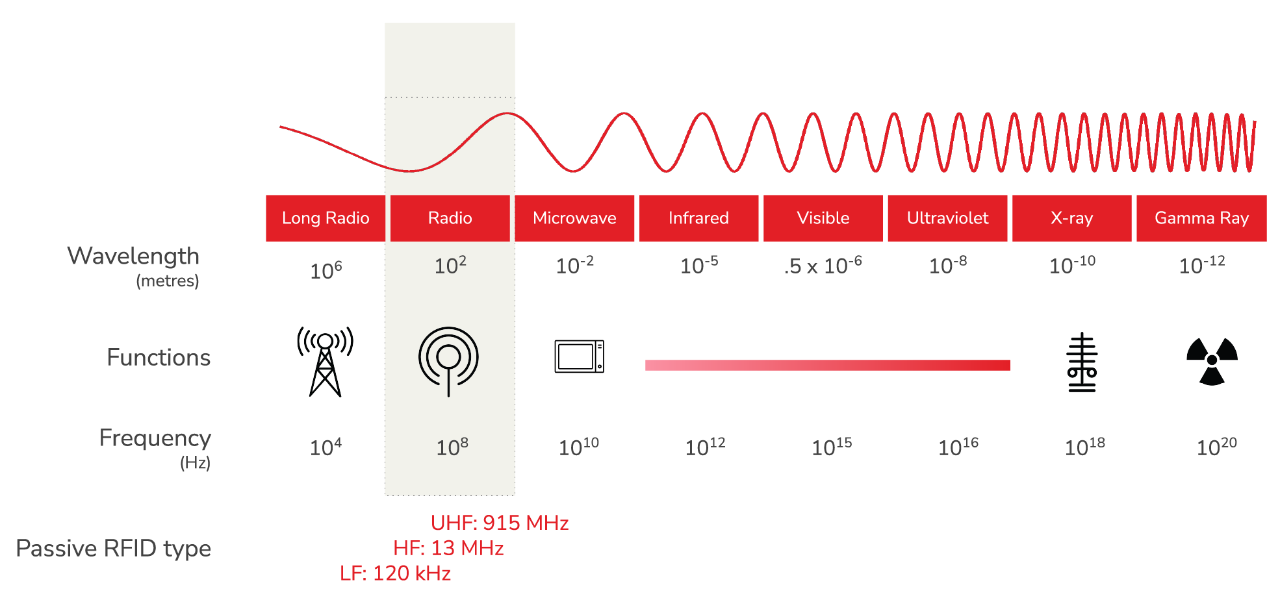
Frequency: Determine the frequency band that is most suitable for your application. The most common frequency bands are low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF).
Operating environment: Consider the operating environment in which the RFID tag will be used, including temperature, humidity, and exposure to physical and chemical elements. This will help you determine the type of tag and inlay that will be able to withstand the conditions.
Tag form factor: Determine the form factor of the tag that is best suited for your application. The form factor can include various shapes and sizes, including round, square, and rectangular. In general, a larger inlay means a larger antenna and better RF performance.
Read range: Consider the read range required for your application. Read range refers to the distance at which an RFID reader can successfully read the information from a tag.
Data storage capacity: Consider the amount of data you need to store on the tag. The data storage capacity of an RFID tag can vary depending on the tag type and inlay.
Cost: Determine your budget for the RFID tags and inlays, taking into account the cost per tag and the volume of tags you need.
Security: Consider the security requirements for your application, such as the need for encryption or password protection for the data stored on the tag.
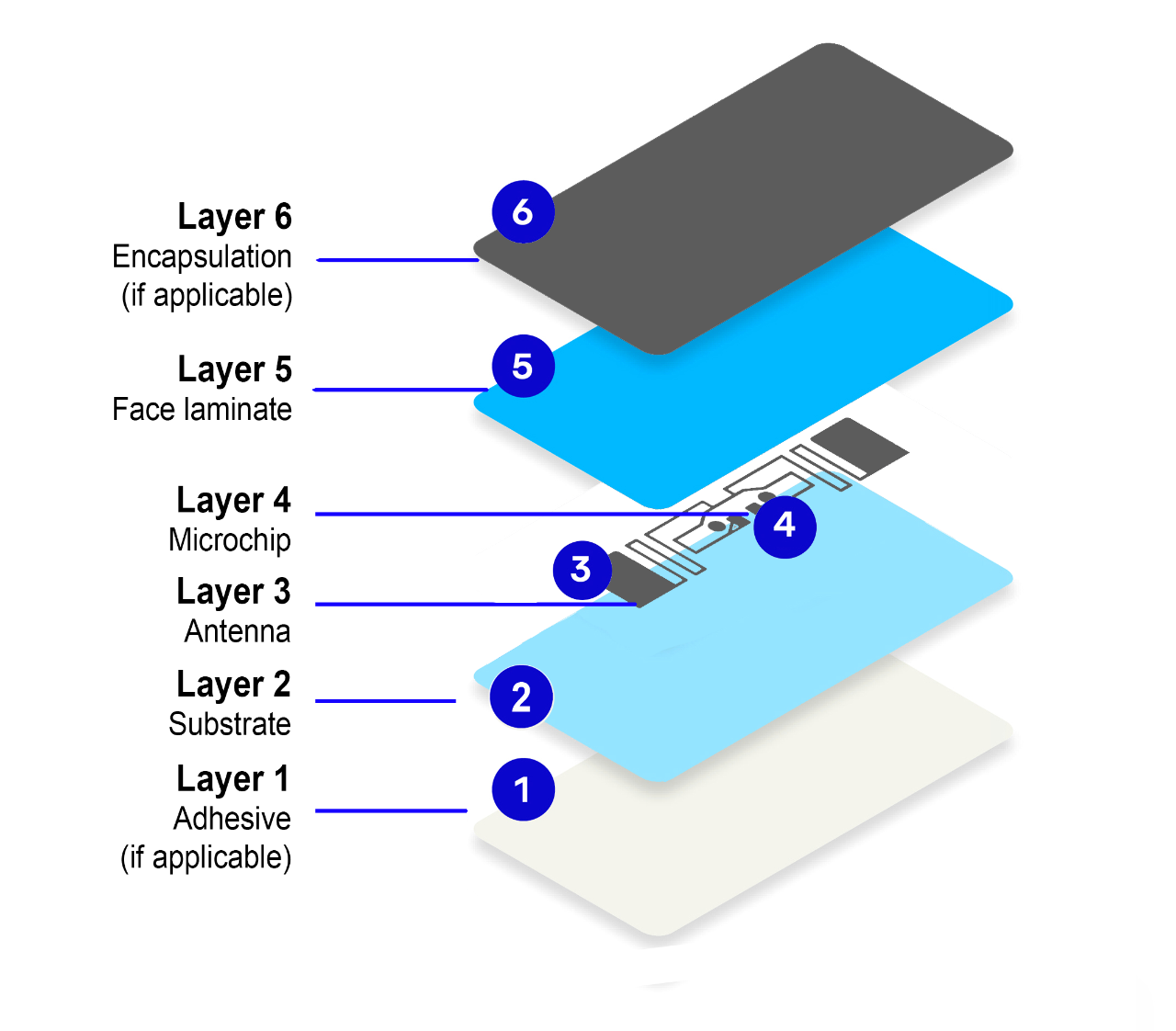
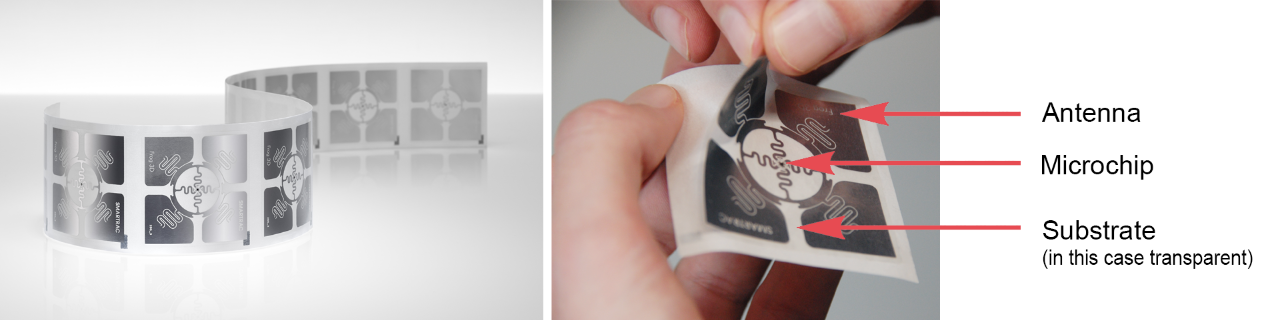
The integrated circuit (IC) of an RFID tag can have a significant impact on the selection of the RFID tag. The IC is the "brain" of the tag and is responsible for storing and processing data, as well as controlling the communication between the tag and the reader.
The IC can influence the selection in several ways:
Memory capacity: The IC determines the amount of memory available for storing data on the tag. If you need to store a large amount of data, you'll need to choose a tag with a larger IC memory capacity.
Read range: The IC can impact the read range of the tag, as different ICs can support different read ranges. If you need to read the tag from a greater distance, you'll need to choose an IC that supports a larger read range.
Operating frequency: Different ICs are designed to operate at different frequencies, so it's important to choose an IC that is compatible with the frequency band used by your RFID reader.
Security: Some ICs include security features, such as encryption, to protect the data stored on the tag. If security is a concern for your application, you'll need to choose an IC that includes these security features.
Cost: The IC can also impact the cost of the tag, as more advanced ICs with larger memory capacities, longer read ranges, and greater security features will be more expensive.
By carefully considering the IC, you can ensure that the tag or inlay you choose will provide the right level of memory capacity, read range, operating frequency, security, and cost for your application.